Android is a free and open-source operating system that runs on mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets. Further, it was developed for smartwatches and Android TV. Each of them has a specialized interface. Android is one of the most popular smartphone operating systems. Android OS was developed by Android Inc., which Google bought in 2005. Various applications like games, music players, cameras, etc. are built for these smartphones and run on Android. The Google Play Store has over 3.3 million apps. Today, Android remains dominant on a global scale. Approximately 75% of the world's population prefers Android to 15% who prefer iOS. It is an operating system that has a huge market for apps.
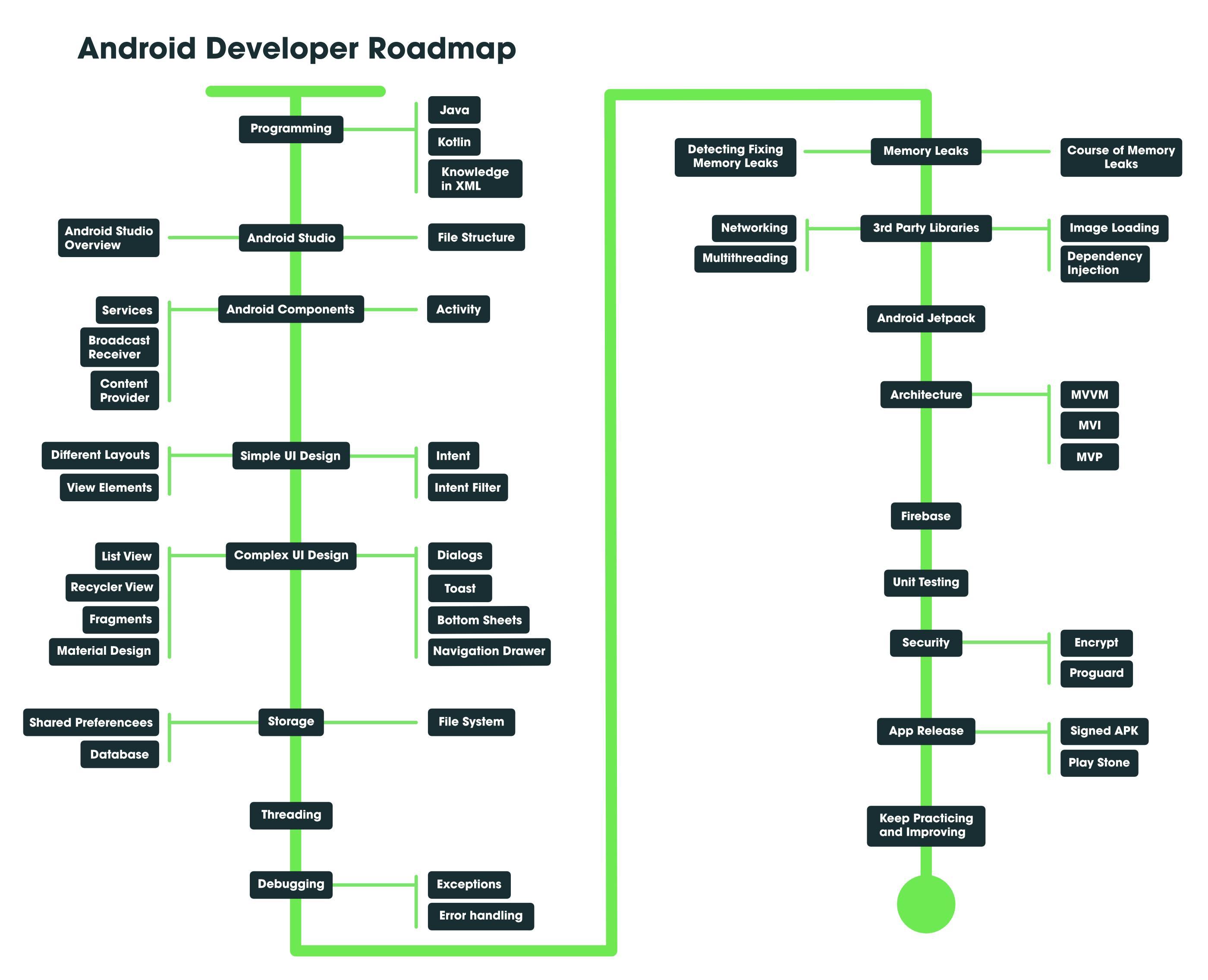
A Roadmap to Learn
Start with an overview of Android. Read some Android-related blogs and also research some Android-related things. For example, read blogs on Introduction to Android Development, History of Android, Different Versions of Android, and topics such as Why Kotlin will replace Java for Android App Development, and so on, to prepare yourself mentally for your journey on Android. Make yourself self-motivated to learn Android and build some awesome projects on it. Do it on a regular basis, and begin learning new Android concepts one at a time. It will be very helpful to join some workshops or conferences on Android before you start your journey. Make your goal clear and move on toward it.
1) Programming Language
Learn these programming languages before you start learning Android.
Java
Kotlin
Sound Knowledge of XML (Extensible Markup Language)
2) Android Studio
It’s better to know your tools before you are going to use it. Android Studio is the official Integrated Development Environment for Google’s Android operating system, built on JetBrains’ IntelliJ IDEA software and designed specifically for Android development.
File Structure:
AndroidManifest.xml file
Java file
Drawable file
Layout file
mipmap file
colors.xml file
strings.xml file
styles.xml file
build.gradle(Module: app) file
Android Studio Overview:
Create a new project
Reopen, close, save the project
Create a new activity, classes, drawable resource files
Run the app on AVD of Emulator or in a real device etc.
3) Android Components
There are some necessary building blocks that an Android application consists of. These loosely coupled components are bound by the application manifest file, which contains a description of each component and how they interact.
Activity:
Activity life cycle
Handle Activity State Changes
Understand Tasks and Back Stack
Processes and Application Lifecycle
Services:
Types of Android Services
The Life Cycle of Android Services
Content Provider:
Content URI
Operations in Content Provider
Working of the Content Provider
Creating a Content Provider
Broadcast Receiver:
- Implicit Broadcast Exceptions
4) Simple UI Design
After you get an idea about the different components of Android, start exploring some simple UI design, which is given below.
Explore different layouts:
Frame
Linear
Relative
Constraint
View Elements:
TextView
EditText
Buttons
ImageView
Intent:
Implicit
Explicit
Intent Filter
5) Complex UI Design
Once you've mastered simple UI design, you can move on to more complex UI design tasks, such as:
ListView
RecycleVIew
Fragments
Dialogs
Toast
Bottom Sheets
Navigation Drawer
Tabs
Material Design
Some inserting Animations
6) Storage
In Android, there are three types of storage systems:
Shared Preferences
File System
Database
- RoomDB
7) Build
Gradle
Debug/ Release Configuration
8) Threading
Threads
Looper
9) Debugging
Debugging is an essential skill for any developer. So the developer must learn these things:
Exceptions
Error Handling
Logging
Memory Profiling
10) Memory Leaks
Cause of memory leaks
Detecting and fixing memory leaks
Context
11) Third-Party Libraries
Image Loading Libraries
Glide
Picasso
Fresco
COIL
Dependency Injection
- Dragger
Networking
- Retrofit
Multithreading
Coroutines
Rxjava
12) Android Jetpack
On its official site*, it says Android Jetpack is a set of libraries, tools, and architectural guidance to help make it quick and easy to build great Android apps. It provides common infrastructure code so you can focus on what makes your app unique.*
AppCompat library
Architecture components,
Animation and transitions
Android Ktx
Navigation
Paging
Slices
WorkManager
13) Android Architecture
The three famous architecture in the Android world are:
MVVM (Model–View–ViewModel)
MVI (Model-View-Intent)
MVP (Model View Presenter)
14) Firebase
FCM (Firebase Cloud Messaging)
Analytics
Remote Config
App Indexing
15) Unit Testing
Local Unit Testing
Instrumentation Testing
16) Security
Encrypt / Decrypt
Proguard
17) App Release
Signed APK
Play Store
18) Keep Practicing and Read Some Android Tips
“Practice makes a man perfect" which explains the importance of continuous practice in any subject to learn anything. So keep practicing and read some Android tips. Below is a complete diagrammatical representation of the Android Roadmap.
More information will be available on the below official page:
https://developer.android.com/courses

